What is a Quantum Dataset?¶
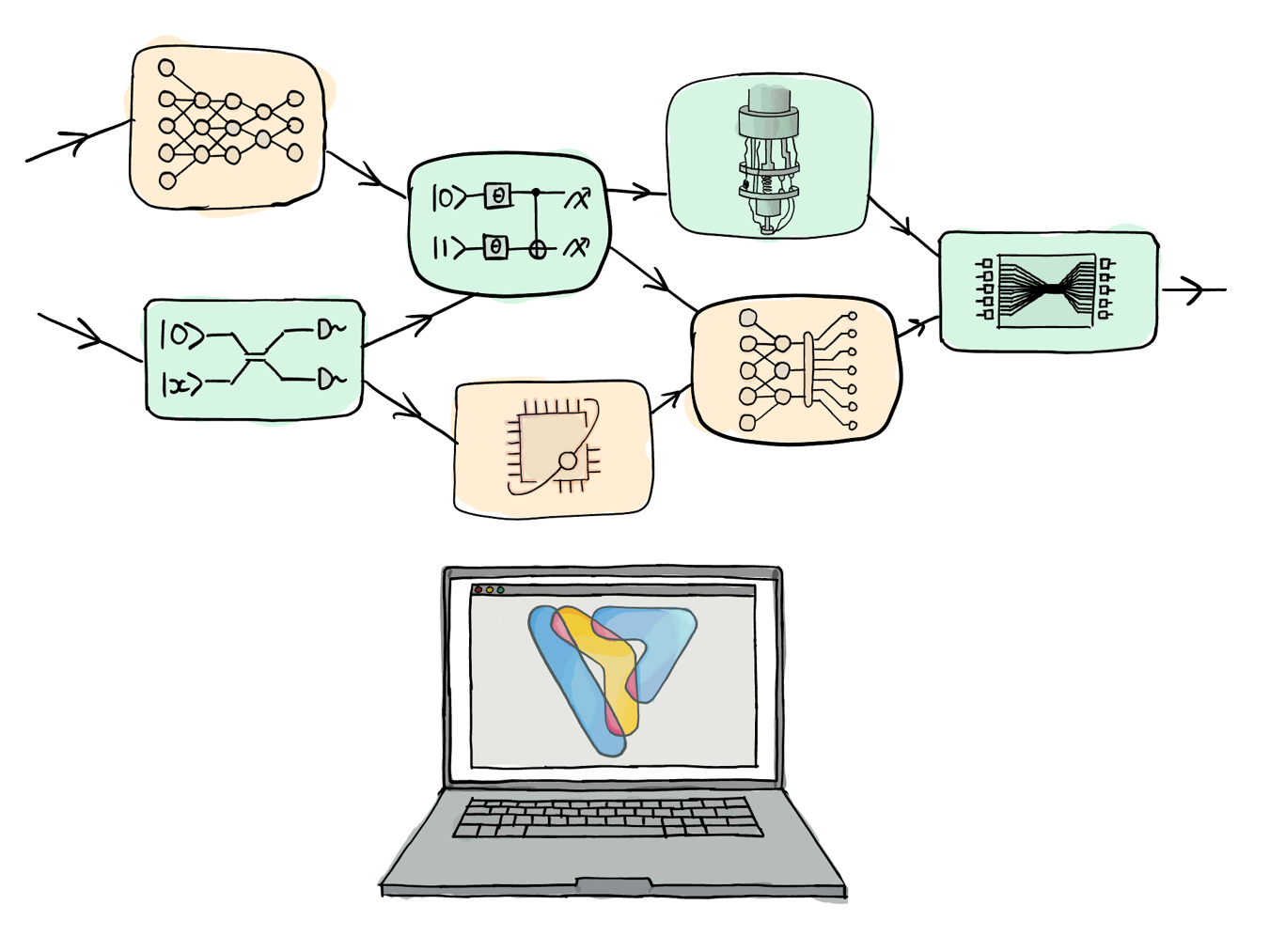
A quantum dataset is a collection of data that describes quantum systems and their evolution. We refer to such data features as quantum data, which in the context of quantum programming, can be realized as the input arguments and outputs of a quantum function that defines a quantum system.
Examples of quantum data¶
Examples of quantum data include the following:
Hamiltonian of the system and any other observables for other relevant properties of interest.
Quantum state of interest, such as the ground state, and an efficient state-preparation circuit for it.
Any useful unitary transformations such as the Clifford operator required for qubit tapering.
Measurement or projection operators and any resulting distributions and expectation values that can be extracted for the system.
Control parameters for system evolution and data related to noise descriptions such as the Kraus operators for channels.
Motivation for Quantum Datasets¶
A lesson from the success of machine learning: easily-accessible, high-quality datasets catalyze the development of new algorithms and the improvement of older ones.
Challenge of achieving quantum advantage: learning from quantum data is more intuitive for quantum computers, leading to an ideal candidate for quantum computational advantage.
Never-ending quest for useful research: readily available data reduces the work required for collaboration between different disciplines, fostering advancements in algorithmic techniques.
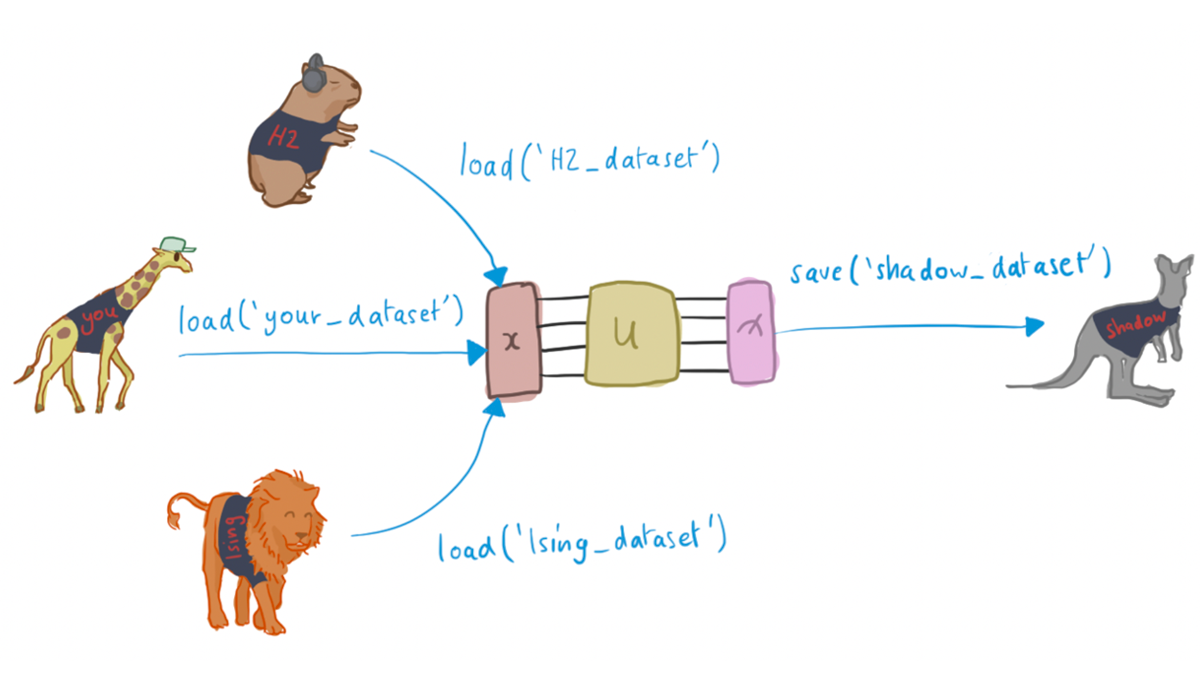
Exploring quantum datasets using PennyLane¶
PennyLane is an open-source software framework built around the concept of quantum differentiable programming, seamlessly integrating quantum simulators and hardware with machine-learning libraries.
PennyLane datasets allow you to develop novel algorithms and benchmark them against problems in applied quantum computation, such as the simulation of physical systems.
For more information on accessing hosted data from PennyLane, please see the PennyLane Documentation.